
DSM Online Support
Support Master
Welcome to DSM Online
How can I help you today
How can we assist you? please let us know the support you need from DSM Online
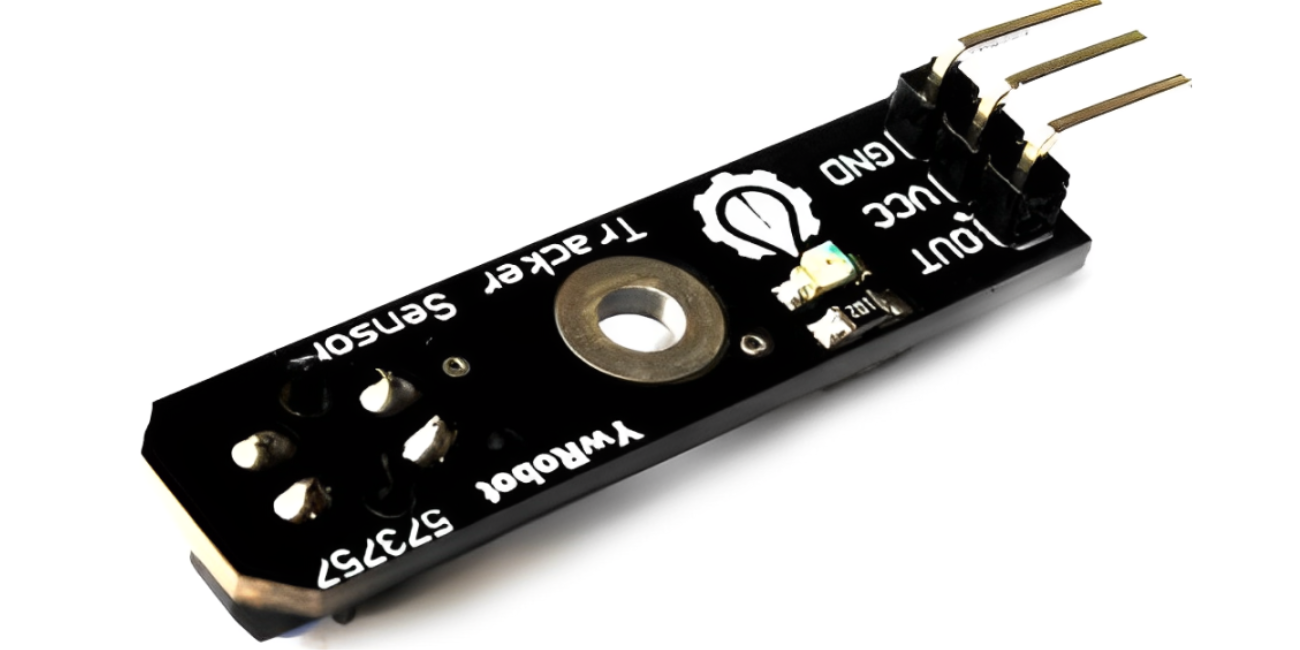
Ever watched a robot flawlessly follow a line on the floor, or magically stop just before bumping into an obstacle? It often feels like magic, but behind that smooth, intelligent movement lies a remarkably simple and effective piece of technology: the IR tracker sensor. These little gadgets are the unsung heroes of countless robotics and automation projects, giving your creations the ability to "see" what's directly in front of them using invisible light.
If you're diving into the world of DIY electronics, building your first robot, or just curious about how machines perceive their environment, understanding the IR tracker sensor is a fantastic place to start. It's a fundamental component that opens up a world of possibilities for robotics projects and beyond.
What Exactly is an IR Tracker Sensor?
At its heart, an IR tracker sensor is a pair of specialized components: an Infrared (IR) LED and an IR photodiode.
The Emitter (IR LED): This is like a tiny flashlight that emits light, but it's infrared light – meaning it's invisible to the human eye. Think of it as a stealthy beam.
The Receiver (IR Photodiode): This component is designed to detect that specific infrared light.
When the invisible IR light emitted by the LED hits a surface, some of it reflects back. If this reflected light is strong enough and hits the photodiode, the sensor "sees" it. The magic lies in how the sensor module then interprets this.
Most common IR tracker sensors are designed as active sensors, meaning they both emit and detect their own infrared light. They typically come as a small module with both the emitter and receiver side-by-side, along with some conditioning circuitry and an adjustable potentiometer for sensitivity. This makes them incredibly easy to integrate into your Arduino IR sensor or ESP32 robotics setups.
How Does This "Invisible Eye" Work in Practice?
Imagine you have a robot that needs to follow a black line on a white floor.
When the infrared sensor is over the white surface, a lot of the IR light reflects back to the photodiode. The sensor's output (often a digital signal) will switch to one state (e.g., HIGH).
When the sensor moves over the black line, black surfaces absorb more light and reflect less. Consequently, less (or no) IR light bounces back to the photodiode. The sensor's output will switch to the other state (e.g., LOW).
By reading these simple HIGH/LOW signals with your microcontroller, your robot knows whether it's on or off the line, allowing it to adjust its movement and follow the path precisely. This same principle applies to obstacle avoidance sensors and general object detection sensors.
Key Features That Make Them So Useful:
Digital Output: Most basic IR tracking modules provide a simple digital output (HIGH or LOW), making them incredibly easy to interface with any microcontroller. No complex analog-to-digital conversions needed for basic operation!
Adjustable Sensitivity: A small potentiometer on the module allows you to fine-tune the sensor's sensitivity. This is vital for adapting to different lighting conditions, surface types (e.g., how reflective the floor is), and desired detection ranges.
Compact Size: They are usually very small and lightweight, perfect for even tiny robot chassis or space-constrained projects.
Cost-Effective: These sensors are typically very affordable, making them a great starting point for beginners or for projects requiring multiple detection points.
Unleashing Your Creativity: Common Applications
The versatility of the IR tracker sensor is truly impressive:
Line Following Robots: This is the classic application! Multiple line follower sensors arranged in an array allow a robot to navigate complex paths by staying precisely on a line.
Obstacle Avoidance Robots: Place an obstacle avoidance sensor on the front of your robot, and it can detect walls, furniture, or even pets, causing it to stop or change direction, making your robot "smart."
Basic Proximity Sensing: Use it as a simple proximity sensor to detect when an object is within a certain range. Think automated hand sanitizers or smart bins.
Object Counting: Position the sensor at an entry point, and each time an object passes, it registers a "count." Great for simple automation tasks.
Edge Detection: Similar to line following, but used to prevent robots from falling off tables or platforms by detecting the absence of a surface.
Simple Automation: Turning on a light when a hand is waved, triggering an alarm when an object is placed, or even basic security systems.
Getting Started: Tips for Using Your IR Tracker Sensor
Power Carefully: Ensure you supply the correct voltage (usually 3.3V or 5V, depending on the module) to the sensor.
Adjust Sensitivity: Don't skip this step! Use the onboard potentiometer to calibrate the sensor for your specific environment and surface types. Test it under different conditions (e.g., over the line/obstacle, away from it) to find the sweet spot.
Mind the Ambient Light: Strong direct sunlight or very bright incandescent lights can sometimes interfere with IR sensors, as they emit IR light themselves. For critical applications, consider shielding the sensor or testing in your target environment.
Surface Reflectivity: Different colors and materials reflect IR light differently. White surfaces are generally good reflectors, while matte black surfaces absorb IR light. Shiny or transparent surfaces can also behave unexpectedly.
Placement is Key: For line following, ensure the sensor is close enough to the line. For obstacle avoidance, position it where it can best "see" incoming obstacles without triggering on the ground.
Conclusion: Your Gateway to Smarter Machines
The IR tracker sensor might be small and deceptively simple, but its power to enable your robots and automated systems to interact with their physical environment is immense. Whether you're building a competitive line follower robot, a friendly robot that avoids bumping into things, or simply exploring the fundamentals of robotics sensors, this infrared tracking module is an indispensable tool. It's affordable, easy to use, and opens up a fantastic avenue for learning and innovation in the exciting world of smart robotics. So, grab an IR sensor, hook it up to your microcontroller, and give your project the gift of "sight"!Okay, let's craft a blog post about IR tracker sensors that feels like a genuine conversation, packed with useful info and those all-important SEO keywords, to help your website climb Google's ranks!
Ever watched a robot flawlessly follow a line on the floor, or magically stop just before bumping into an obstacle? It often feels like magic, but behind that smooth, intelligent movement lies a remarkably simple and effective piece of technology: the IR tracker sensor. These little gadgets are the unsung heroes of countless robotics and automation projects, giving your creations the ability to "see" what's directly in front of them using invisible light.
If you're diving into the world of DIY electronics, building your first robot, or just curious about how machines perceive their environment, understanding the IR tracker sensor is a fantastic place to start. It's a fundamental component that opens up a world of possibilities for robotics projects and beyond.